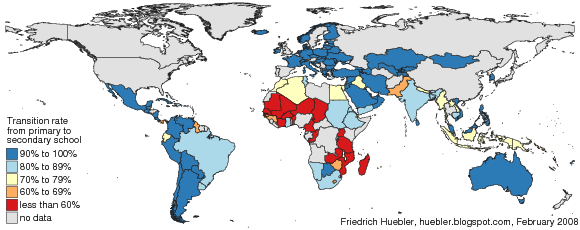
UNICEF has released the first datasets from the third round of Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS), conducted in 2005 and 2006. The first round of MICS surveys was carried out around 1995, followed by a second round of surveys around 2000.
MICS surveys are nationally representative household surveys that were developed by UNICEF in collaboration with other organizations to collect data on the situation of children and women. The most recent round of surveys collected data on household characteristics, education, child labor, water and sanitation, child mortality, maternal and newborn health, knowledge of HIV and AIDS, contraceptive use, birth registration, and other areas. The data can be used to track progress toward the UN Millennium Development Goals and other goals. The MICS program is described in detail on the Childinfo website of UNICEF.
In the area of education, the latest MICS surveys provide data for the following household member characteristics:
The MICS datasets are available for download in SPSS format from the Childinfo website. The datasets are provided free of charge but interested researchers have to apply for a MICS username and password. At the time of writing, datasets from the following countries were available: Bangladesh, Belarus, Côte d'Ivoire, Cuba, Jamaica, Mongolia, Montenegro, Serbia, Sierra Leone, and Uzbekistan. In addition, survey questionnaires, survey reports, and a set of standard tabulations are provided. The questionnaires, tables, and reports can be downloaded without access restrictions.
External links
Related articles
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/02/unicef-releases-new-mics-survey-data.html
MICS surveys are nationally representative household surveys that were developed by UNICEF in collaboration with other organizations to collect data on the situation of children and women. The most recent round of surveys collected data on household characteristics, education, child labor, water and sanitation, child mortality, maternal and newborn health, knowledge of HIV and AIDS, contraceptive use, birth registration, and other areas. The data can be used to track progress toward the UN Millennium Development Goals and other goals. The MICS program is described in detail on the Childinfo website of UNICEF.
In the area of education, the latest MICS surveys provide data for the following household member characteristics:
- highest level of education
- current school attendance
- school attendance in the previous year
- literacy
The MICS datasets are available for download in SPSS format from the Childinfo website. The datasets are provided free of charge but interested researchers have to apply for a MICS username and password. At the time of writing, datasets from the following countries were available: Bangladesh, Belarus, Côte d'Ivoire, Cuba, Jamaica, Mongolia, Montenegro, Serbia, Sierra Leone, and Uzbekistan. In addition, survey questionnaires, survey reports, and a set of standard tabulations are provided. The questionnaires, tables, and reports can be downloaded without access restrictions.
External links
Related articles
- Education data from household surveys
- Education country profiles by UNICEF
- Primary school attendance in India, 2000
- Secondary school attendance in India, 2000
- Educational attainment in India, 1950-2000
- Primary school completion in India, 1950-2000
- India has 21 million children out of school in 2006
- Child labor and school attendance in Bolivia, 2000
- Child labor and school attendance in Bolivia, 2000, part 2
- Years of schooling and literacy: Can everyone with primary education read and write?
- Years of schooling and literacy, part 2
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/02/unicef-releases-new-mics-survey-data.html