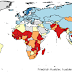
UNICEF estimates that 93 million children of primary school age were out of school in 2006. The graph below presents the regional distribution of these children according to the country classification used by UNICEF. The majority of children out of school, 41 million, lived in Sub-Saharan Africa, the region with the world's lowest primary school enrollment rates. In South Asia, 32 million children were out of school, most of them in India, the country with the world's largest population of children not in school.
In other regions, fewer children of primary school age were not in school. The Middle East and North Africa, East Asia and the Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, the industrialized countries, and the countries of Central and Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) combined account for 20 million children out of school, only one fifth of the global number.
Estimates for individual countries are available on the Childinfo website of UNICEF. The site also describes the data sources and methodology for UNICEF's calculation of the number of children out of school.
Regional distribution of children of primary school age out of school (in millions), 2006

Source: UNICEF, 2007, Progress for Children.
References
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/03/regional-distribution-of-children-out.html
In other regions, fewer children of primary school age were not in school. The Middle East and North Africa, East Asia and the Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, the industrialized countries, and the countries of Central and Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) combined account for 20 million children out of school, only one fifth of the global number.
Estimates for individual countries are available on the Childinfo website of UNICEF. The site also describes the data sources and methodology for UNICEF's calculation of the number of children out of school.
Regional distribution of children of primary school age out of school (in millions), 2006

Source: UNICEF, 2007, Progress for Children.
References
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF). 2007. Progress for children: A World Fit for Children statistical review. New York: UNICEF. (Download PDF, 3.6 MB)
- Universal primary education by 2015: A goal out of reach?
- Global population of primary school age, 2000-2015
- Population structure and children out of school
- India has 21 million children out of school
- 115 million children out of school in 2002
- Global trends in primary and secondary education, 2000-2004
- Trends in primary school enrollment, 1970-2004
- Primary school enrollment in 2004
- Millennium Development Goal regions and UNICEF regions
- UNICEF statistical review: Progress for Children
External links
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/03/regional-distribution-of-children-out.html