Pupils can be overage for their grade for two reasons: late entry and repetition. Take for example a country where children are expected to enter primary school at 6 years of age. If a child enters grade 1 at age 7, he or she is one year overage for the grade. A child who enters grade 1 at age 8 and repeats the grade will be three years overage for the grade; two of the three years are due to late entry and the third year is due to repetition.
Children who are many years overage are less likely to complete their education. If they stay in school, they graduate later than pupils who entered school at the official starting age. These overage graduates enter the labor market late and often with lower educational attainment. As a consequence, they are likely to have lower cumulative earnings over their lifetime than persons who graduated and entered the labor market at a younger age and with higher educational attainment. For the country as a whole this in turn means reduced national income and slower economic growth.
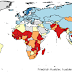
Overage school attendance is common in sub-Saharan Africa but also occurs in other regions. The figure below shows data from 36 nationally representative household surveys that were conducted between 2004 and 2009. 34 of these surveys were Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and the remaining two surveys, those for Bangladesh and Kyrgyzstan, were Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS). For each country, the graph shows the share of children in primary and secondary education who are at least one or two years overage for their grade. The entrance ages and durations of primary and secondary education used in this study are those specified by the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED).
Percentage of children in primary and secondary education who are at least 1 or 2 years overage for their grade

Source: Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS), 2004-2009.
In the sample of 36 countries, the share of children who are at least one year overage for their grade ranges from 5 percent in Armenia to 95 percent in Haiti. Other countries where at least three out of four pupils in primary or secondary education are overage include Liberia (93%), Uganda (86%), Rwanda (83%), Cambodia (78%), Mozambique (76%), and Ethiopia (75%). In addition to Armenia, the percentage of pupils who are at least one year overage is below 10 percent in Moldova and Egypt (8%).
The share of children in primary and secondary education who are at least two years overage for their grade ranges from 1 percent in Armenia to 85 percent in Haiti. In addition to Haiti, at least half of all pupils are two or more years overage in Liberia (84%), Uganda (67%), Rwanda (65%), Ethiopia (59%), Cambodia (55%), Malawi (51%), and Madagascar (50%). On average, the share of children who are at least two years overage is 19 percent less than the share of children who are at least one year overage.
However, there are exceptions. In Albania and the Ukraine, 43 and 26 percent respectively of all children in primary and secondary education are at least one year overage. By contrast, only 5 and 2 percent respectively are at least two years overage. This means that in these two countries, a relatively large number of children enter school one year late or repeat one grade, but hardly any children enter school two years late or repeat more than one grade. Late entry and repetition are therefore less likely to have negative consequences on lifetime earnings and national income in Albania and the Ukraine than in other countries.
Related articles
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2011/06/age.html
Children who are many years overage are less likely to complete their education. If they stay in school, they graduate later than pupils who entered school at the official starting age. These overage graduates enter the labor market late and often with lower educational attainment. As a consequence, they are likely to have lower cumulative earnings over their lifetime than persons who graduated and entered the labor market at a younger age and with higher educational attainment. For the country as a whole this in turn means reduced national income and slower economic growth.
Overage school attendance is common in sub-Saharan Africa but also occurs in other regions. The figure below shows data from 36 nationally representative household surveys that were conducted between 2004 and 2009. 34 of these surveys were Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and the remaining two surveys, those for Bangladesh and Kyrgyzstan, were Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS). For each country, the graph shows the share of children in primary and secondary education who are at least one or two years overage for their grade. The entrance ages and durations of primary and secondary education used in this study are those specified by the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED).
Percentage of children in primary and secondary education who are at least 1 or 2 years overage for their grade

Source: Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS), 2004-2009.
In the sample of 36 countries, the share of children who are at least one year overage for their grade ranges from 5 percent in Armenia to 95 percent in Haiti. Other countries where at least three out of four pupils in primary or secondary education are overage include Liberia (93%), Uganda (86%), Rwanda (83%), Cambodia (78%), Mozambique (76%), and Ethiopia (75%). In addition to Armenia, the percentage of pupils who are at least one year overage is below 10 percent in Moldova and Egypt (8%).
The share of children in primary and secondary education who are at least two years overage for their grade ranges from 1 percent in Armenia to 85 percent in Haiti. In addition to Haiti, at least half of all pupils are two or more years overage in Liberia (84%), Uganda (67%), Rwanda (65%), Ethiopia (59%), Cambodia (55%), Malawi (51%), and Madagascar (50%). On average, the share of children who are at least two years overage is 19 percent less than the share of children who are at least one year overage.
However, there are exceptions. In Albania and the Ukraine, 43 and 26 percent respectively of all children in primary and secondary education are at least one year overage. By contrast, only 5 and 2 percent respectively are at least two years overage. This means that in these two countries, a relatively large number of children enter school one year late or repeat one grade, but hardly any children enter school two years late or repeat more than one grade. Late entry and repetition are therefore less likely to have negative consequences on lifetime earnings and national income in Albania and the Ukraine than in other countries.
Related articles
- Official school ages: primary, secondary, and compulsory education
- Primary school entrance age and duration
- Repetition rates in primary and secondary school
- Survival rate to the last grade of primary school
- Transition from primary to secondary education
- Regional disparities in school life expectancy
- Children of primary and secondary school age out of school
- Children out of school: Global trend 1999-2008
- Household wealth and years of education
- National wealth and years of education
- National wealth and school enrollment
- Poverty and educational attainment in the United States
- Poverty and educational attainment in the United States, part 2
- Review of the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED)
- Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS)
- Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS)
- International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED)
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2011/06/age.html