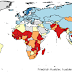
In secondary school, pupil/teacher ratios are lower than in primary school. The Data Centre of the UNESCO Institute for Statistics provides the pupil/teacher ratio in secondary school for 189 countries and territories. For 100 countries, the pupil/teacher ratios are from 2006, 9 countries have data from 2007, 51 countries have data from 2004 or 2005, and the remaining 29 countries have data from 1999 to 2003. For the map below, all countries with data were divided into five groups:
- Fewer than 10 pupils per teacher: 24 countries
- 10 to 19 pupils per teacher: 107 countries
- 20 to 29 pupils per teacher: 41 countries
- 30 to 39 pupils per teacher: 13 countries
- 40 or more pupils per teacher: 4 countries

Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics, Data Centre, May 2008.
The lowest pupil/teacher ratios in secondary school were reported for Bermuda (6.0), Tokelau (7.0), Portugal (7.1), and Andorra (7.8). 20 additional countries have pupil/teacher ratios above 8 and below 10: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Croatia, Georgia, Greece, Kuwait, Lebanon, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Malta, Monaco, Niue, Norway, Qatar, Russia, Sweden, and Turks and Caicos Islands.
More than half of all countries - including most countries in North and South America, Europe, the Middle East, and East Asia - have pupil/teacher ratios between 10 and 19. The group also includes some countries in other regions. Although pupil/teacher ratios in Sub-Saharan Africa are generally higher than in other parts of the world, the following countries from the region have only 10 to 19 pupils per secondary school teacher: Angola, Botswana, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Comoros, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Mauritius, Seychelles, and Swaziland. 22 of the 41 countries with pupil/teacher ratios between 20 and 29 are also located in Sub-Saharan Africa.
17 countries have 30 or more pupils per teacher in secondary school and 10 of these countries are in Sub-Saharan Africa. The countries with 30 to 39 pupils per teacher are Chad, Congo, Djibouti, Honduras, India, Kenya, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nepal, Nicaragua, Philippines, South Africa, and Zambia. Classes at the secondary level of education are most crowded in Nigeria (pupil/teacher ratio 40.2), Pakistan (41.9), Malawi (45.6), and Eritrea (54.4).
The following table lists the average pupil/teacher ratio in secondary school by Millennium Development Goal region. The Commonwealth of Independent States (10.9), the developed countries (11.4), Oceania (14.8), Western Asia (15.3), Latin America and the Caribbean (16.6), Eastern Asia (19.0), and Northern Africa (19.0) have average pupil/teacher ratios below 20. Pupil/teacher ratios are highest in South-Eastern Asia (22.8), Sub-Saharan Africa (25.8), and Southern Asia (26.4). The global average is 18.0 pupils per teacher in secondary school. These average values are unweighted, which means that each country is given the same weight within its region, regardless of the size of its population.
Average pupil/teacher ratio in secondary school by MDG region, circa 2006
| MDG region | Pupil/teacher ratio |
| Developed countries | 11.4 |
| Commonwealth of Independent States | 10.9 |
| Eastern Asia | 19.0 |
| South-Eastern Asia | 22.8 |
| Oceania | 14.8 |
| Southern Asia | 26.4 |
| Western Asia | 15.3 |
| Northern Africa | 19.0 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 25.8 |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 16.6 |
| World | 18.0 |
The data analyzed in this article can be downloaded from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics Data Centre, under Predefined Tables - Education - Table 11: Indicators on teaching staff at ISCED levels 0 to 3.
Related articles
- Pupil/teacher ratio in primary school
- UNESCO releases data from 2007 education survey
- Millennium Development Goal regions and UNICEF regions
Friedrich Huebler, 16 November 2008, Creative Commons License
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/11/ptr.html